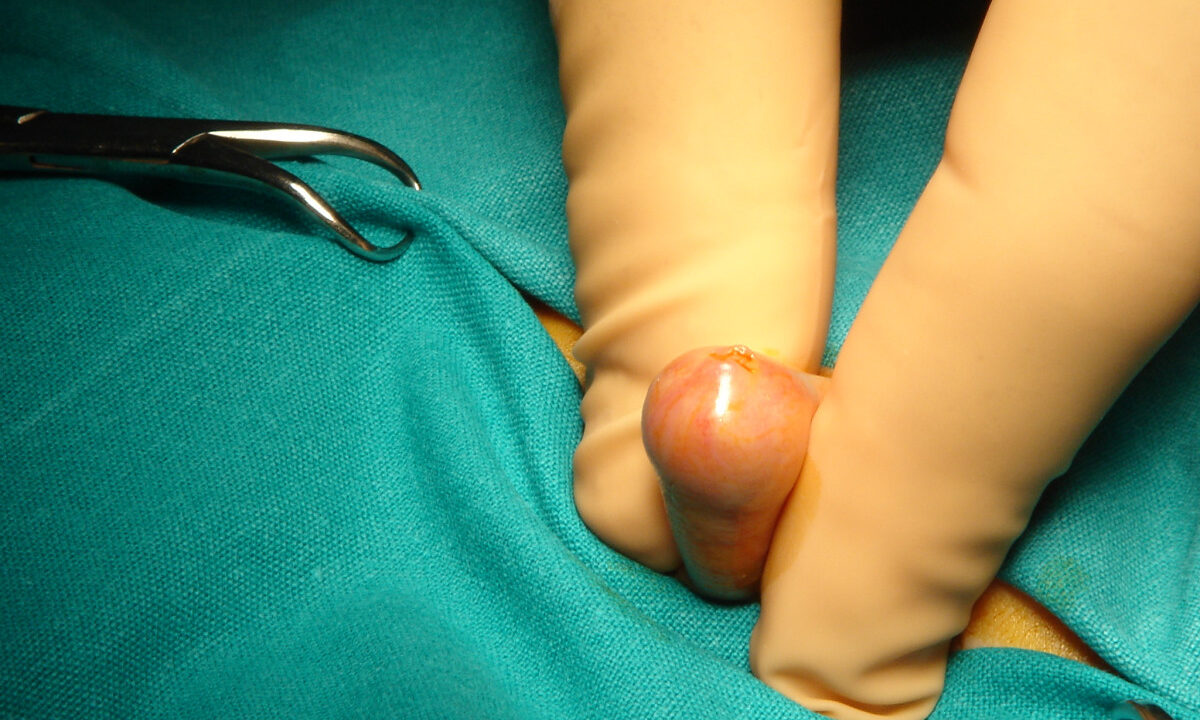
Phimosis is inability to retract the foreskin of the glans penis
Types
- Physiologic phimosis- in newborns
- Pathologic phimosis- due to scarring secondary to infection, inflammation or trauma
Clinical presentation
- New-onset non-retractability of the foreskin
- Ballooning of prepucal skin on urination
- Painful erection
- Bleeding from the foreskin orifice
- Recurrent inflammation
- Dysuria
- Discharge
Investigations
- Urinalysis- look for evidence of infection
- Full blood count- leukocytosis in infection
Management
- Dilatation with artery forceps
- Incision of the dorsal hood
- Circumcision
- 0.5% betamethasone cream applied bd for 6 weeks around the phimotic ring
- Stretching exercises of the foreskin
Complications
Increased risk of;
- Paraphimosis
- BXO( Balanitis Xerotica Obliterans)
- Severe balanoposthitis
- Recurrent urinary tract infection