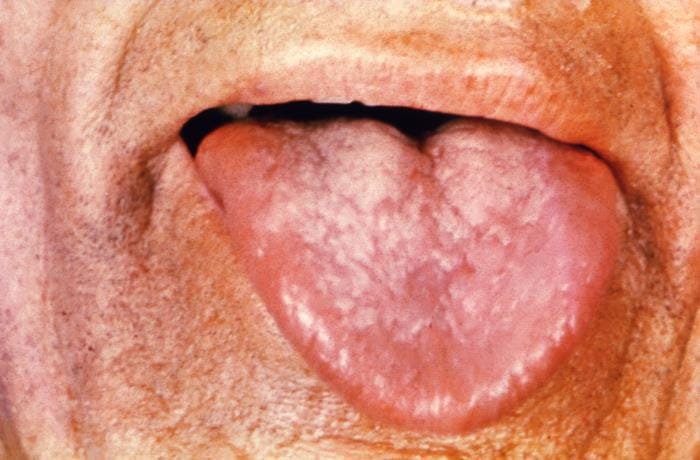
Leukoplakia is a potentially malignant disorder that most commonly affects the oral cavity. Oral hairy leukoplakia is a separate disorder that is not premalignant and occurs in immunocompromised individuals
Risk factors
- Tobacco use
- Alcohol use
- Association with HPV infection
Clinical presentation
-White patches that cannot be scraped off.
-Clinically classified into two types;
- Homogenous- a uniformly white, thin plaque with well-defined margins
- Nonhomogeneous- can present as;
- Speckled lesions
- Erythroleukoplakia
- Granular, nodular or verrucous, white lesions
*Nonhomogenous type carries more risk for cancer. Some patients will develop squamous cell carcinoma.
Predictors of cancer
- Nonhomogeneous type
- Large size >4cm in the largest diameter
- Localization in the lateral border of the tongue and floor of the mouth
- Extension over more than one anatomical site
- Presence of dysplasia on histology
Diagnosis
-A definitive diagnosis requires a biopsy for histopathological examination
-Histopathological features;
- Parakeratosis, hyperkeratosis, atrophy, inflammation, hyperplasia without dysplasia, or dysplasia
- Epithelial dysplasia, squamous cell carcinoma(SCC) in situ, or invasive SCC have been reported.
Management
- Destructive therapies- laser ablation, cryosurgery
- Medical therapy- retinoids, vitamin A, carotenoids, NSAIDs
- Watchful waiting
- Surgery- cold scalpel excision, laser excision
Differential diagnosis
- Oral hairy leukoplakia
- Frictional keratosis
- Lichen planus
- Discoid lupus erythematosus
- Candidiasis
Prognosis
- Local recurrence and SCC occur despite surgical removal
- Follow up every three months in the first year after surgery. Once per year thereafter if no recurrence or development of new mucosal lesions