- Home
- INTERNAL MEDICINE
- Measles
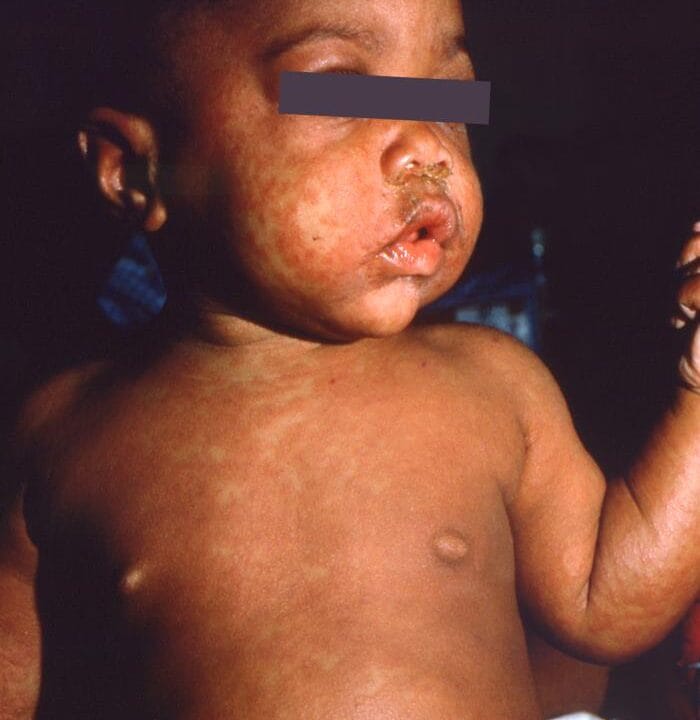
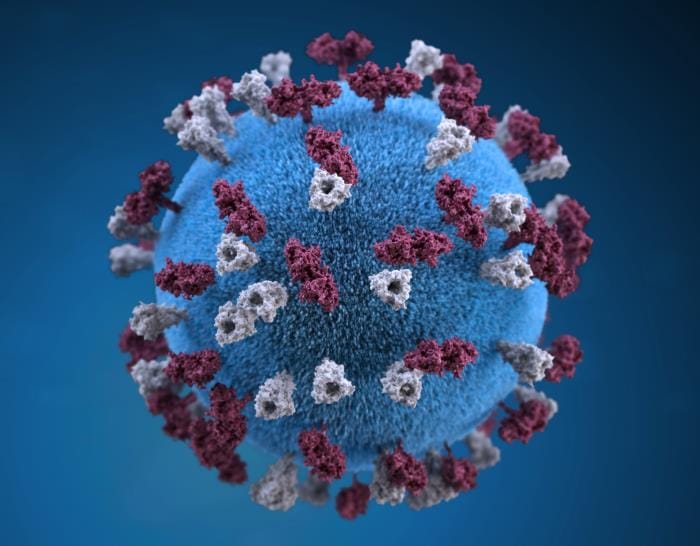
Measles is a systemic infection caused by the measles virus. Spread via respiratory droplets. The incubation period is 6-19 days
Clinical presentation
- Prodromal period 1 to 3 days before the rash, characterized by upper respiratory symptoms, conjunctivitis, and Koplik spots
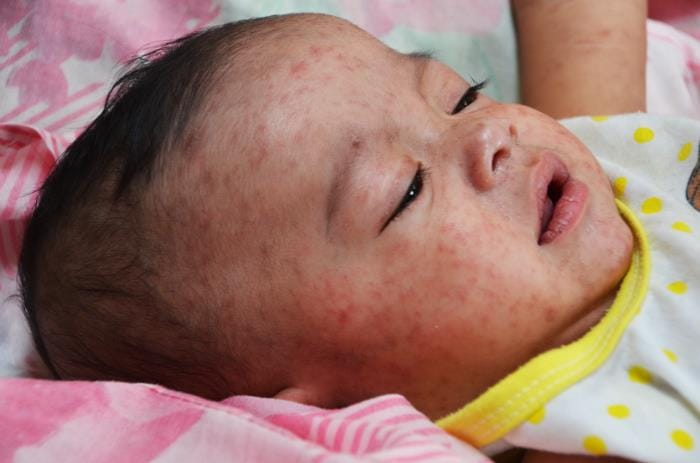
- Rash- maculopapular and spreads from the face to the extreme ties
- Generalized lymphadenopathy and diarrhea
- Atypical presentation is found in the poorly nourished, immunocompromised, or vitamin deficient. The rash is absent and presents with encephalitis or pneumonitis.
- May exacerbate tuberculosis
- Maybe severe in pregnant women
- Mortality is mainly at extremes of age
Diagnosis
- Mainly clinical
- Serology for IgM antibodies
Management
- Normal immunoglobulin in pregnant women and the immunocompromised, within six days of exposure
- Vitamin A for uncomplicated disease
- Antibiotics for bacterial complications
Complications
- Otitis media
- Bacterial pneumonia
- Pancreatitis and transient hepatitis
- Clinical encephalitis
- Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis( late)
Causes of death
Mainly due to bacterial superinfection;
- Pneumonia
- Diarrhoea
- Noma Oris
- Encephalitis
Prevention
- Vaccination- part of MMR( Measles Mumps Rubella)
- Natural infection confers lifelong immunity