- Home
- INTERNAL MEDICINE
- Chickenpox
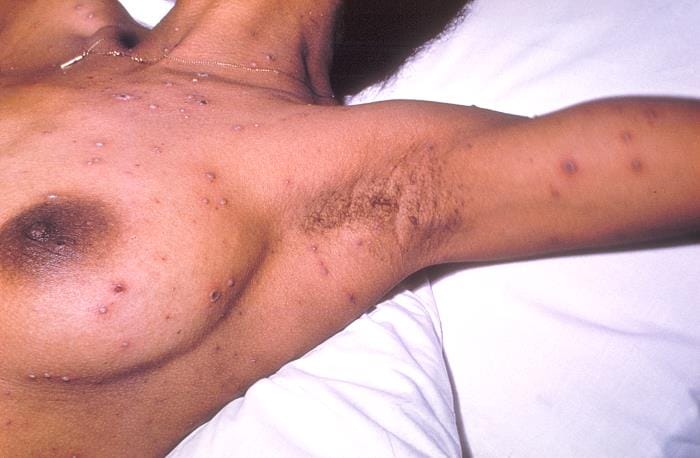
Chickenpox is caused by the varicella-zoster virus, a dermatropic and neurotropic virus. The primary disease occurs in childhood. Can reactivate later.
Spread- aerosol and direct contact. Highly infectious to the non-immune. Well tolerated in children. Severe disease in pregnancy, immunocompromised and adults
Incubation 11-20 days.
Clinical features
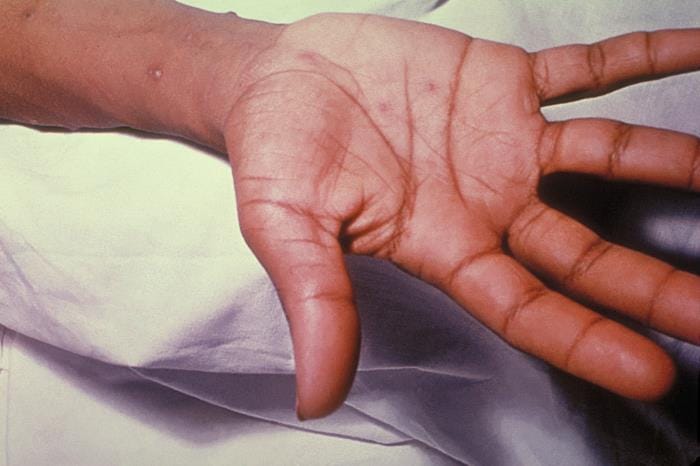
- Vesicular rash that starts on mucosal surfaces then rapidly spreads centripetally.
- New lesions every 2 to 4 days; each crop is associated with fever
- Infectivity- 4 days before rash till last vesicles crust over
- Severe disease- that with visceral involvement
- Maternal infection early in the pregnancy carries a 3% risk of developmental abnormality in the eyes, CNS, and limbs. Within five days of delivery, there’s a severe disease with visceral involvement.
Complications
The most common is a 2⁰ bacterial infection from itching.
Others;
- Self-limiting cerebellar ataxia
- Hepatitis, pneumonia
- Encephalitis
Diagnosis
- Mainly clinical
- DNA or PCR of fluid- detects antigen
- Serology- identify those seronegative at risk of infection
Management
1. Supportive- antihistamines, cropping of fingernails, and acetaminophen in children
2. Antivirals- acyclovir or its analogues
Indications; – an uncomplicated disease in adults
- Complicated disease
- The pregnant and immunocompromised
- Acyclovir 800mg 5 times daily for five days
- Intravenous therapy for severe disease
- Prolonged treatment for the immunocompromised
3. Human Varicella Zoster immunoglobulin. For;
- Those susceptible to infection
- Those at risk for severe disease
- Significant contact with the virus
Given within seven days of exposure
Prevention
1. Vaccination;
- Children – at 1yr and 4 to 6 years old
- Seronegative adults- 2 doses, one month apart
- In planned immunosuppression, e.g., transplant.