- Home
- INTERNAL MEDICINE
- Respiratory system
- Allergic Rhinitis
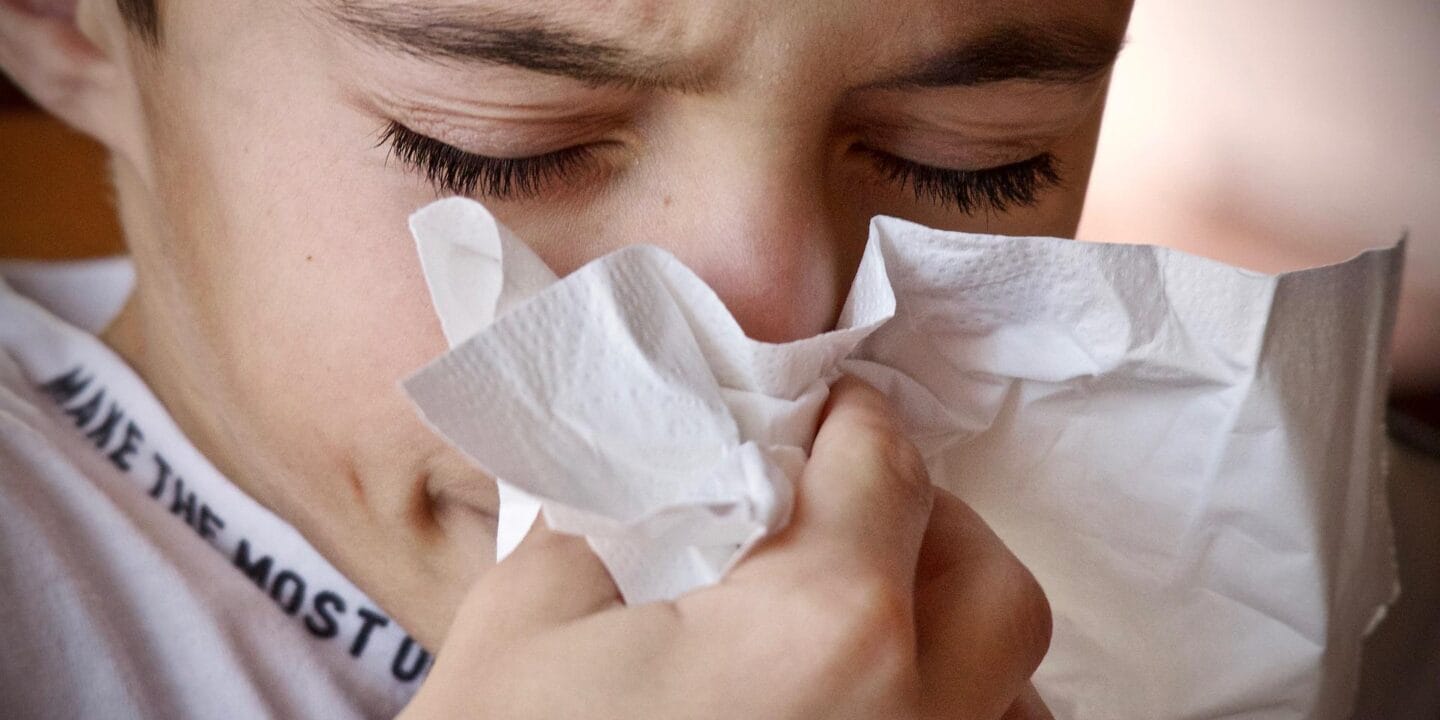

Allergic rhinitis is a disorder marked by episodes of nasal discharge (watery), congestion and sneezing. It may be perennial or seasonal and is caused by an immediate hypersensitivity reaction in the mucosa of the nose.
The most common seasonal type is Hay Fever which occurs mainly in northern Europe. The perennial type is usually a specific antigen reaction from fungal spores, house dust, animal dander and chemical or physical irritants like perfumes and dry or cold atmospheres. (vasomotor rhinitis).
Clinical Features
- Seasonal – sudden, frequent attacks consisting of profuse nasal discharge (watery), obstruction of the nose and
- Sneezing. Accompanied by conjunctival irritation (watery eyes) and smarting, and may last up to
- Few hours
- Perennial symptoms are similar to seasonal but less severe and are mostly continuous.
Investigations
Skin hypersensitivity testing with specified antigen- positive in seasonal type, less beneficial in perennial
Management
1. Removal of dust and proper ventilation for those sensitive to dust
2. Avoidance of pollen and animal dander is, however, impractical
3. For both perennial and seasonal rhinitis, the below are effective either combined or singly
- Antihistamines like loratidine
- Steroid nasal sprays like dipropionate, beclometasone, fluticasone, budesonide or mometasone
- Sodium cromoglicate nasal spray
- If resistant to the above treatment and interfering with daily activities, desensitize with immunotherapy but anticipate
- Severe reaction
- Vasomotor rhinitis-ipratropium bromide thrice daily intranasal.