Trichomoniasis is the most common non viral STD globally and affects females more than males. It is caused by Trichomonas vaginalis, a motile anaerobic protozoan parasite. It’s the most common non-viral STD globally and affects females more than males.
Transmission occurs through sexual contact. It infects the urogenital epithelium of the vagina, urethra and para urethral glands. Less commonly, the cervix, bladder and prostate
Clinical presentation
Often asymptomatic- in 85%
1. Acute infection in females;
- Malodorous, purulent discharge- thin and yellow-green. It’s associated with burning, pruritus, frequency, dysuria or dyspareunia. Post-coital bleeding may occur.
- Worsening of symptoms during menstruation
- Physical examination- erythematous vulva and vaginal mucosa, discharge
- Strawberry cervix- punctate haemorrhages on the vagina and cervix
2. Males;
- >75% are asymptomatic
- Urethritis symptoms- dysuria, mucopurulent or clear discharge. May have a burning sensation and pruritus after sex
Investigations of trichomonas vaginalis
- Microscopy of saline wet mount- motile flagellated organisms
- pH- >4.5
- Nucleic acid amplification tests-the gold standard. Highly sensitive and specific
- Rapid antigen and DNA hybridization probes- in areas of high prevalence where other tests aren’t available
- Culture- not widely available and takes up to 7 days
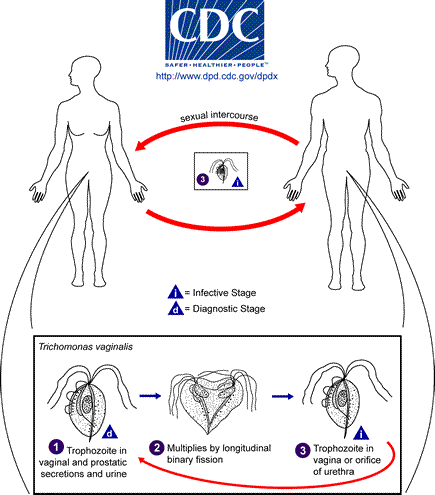
Differential diagnosis
- Candidal vulvovaginitis
- Bacterial vaginosis
- Gonorrhoea, Chlamydia
- Atrophic vaginitis
Management
- Nitroimidazoles
- Metronidazole 400mg bd PO for 5 to 7 days
- Or metronidazole 2g oral stat dose
- Treatment of partners
- Rule out other STDs
- Refractory cases; paromomycin 250mg daily for two weeks
Complications
- Epididymitis
- Prostatitis
- Infertility
- Prostate cancer
- Balanoposthitis
Prevention
- Consistent use of condoms
- Limiting of sexual partners
- Screening for;
- HIV infected women
- HIV non-infected women with multiple partners and a history of STIs