Hemothorax is defined as a collection of f blood within the pleural space
Types
1. Traumatic
- It can be due to blunt or penetrating chest trauma
- A massive hemothorax is due to aortic injury, myocardial rupture, and injuries to hilar structures.
- Other causes are injury to the lung parenchyma and intercostal or mammary blood vessels.
2. Nontraumatic
Causes include;
- Spontaneous pneumothorax- most common
- Malignancy
- Vascular disease
- Endometriosis
- Coagulation disorders
Clinical features
Nontraumatic- signs and symptoms of the underlying disorder. Tachycardia and hypotension, if significant.
Traumatic-
- Dyspnoea, chest pain, hemorrhagic shock, flat chest veins, reduced breath sounds, dullness on percussion, decreased tactile fremitus, crepitus on palpation, reduced chest expansion
Investigations
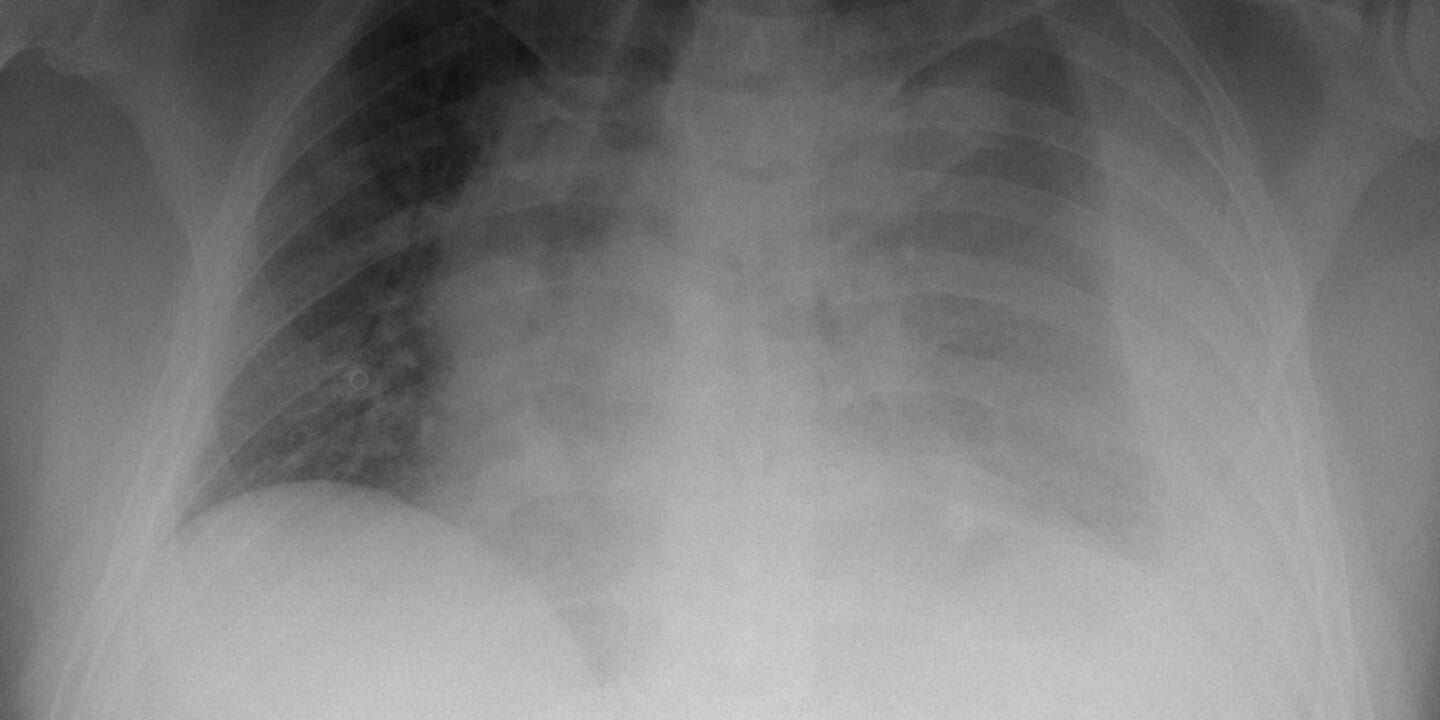
- Chest Xray-
- Opacification
- Blunting of costophrenic angle
- Air fluid level
- Tracheal deviation in a massive hemothorax
* A volume of 300ml is required for hemothorax to manifest on an upright chest Xray
2. Ultrasound-
- Commonly used in the FAST protocol
- Smaller volumes can be detected
- Hyperechogenic signal in the costodiaphragmatic recess
* Features of underlying disease in nontraumatic hemothorax
3. Chest CT – can identify an underlying malignancy
4. Chest CTA- can identify the source of bleeding
5. Pleural fluid analysis
6. Complete blood count
Management
-Stabilize the patient first
-A massive hemothorax is a life-threatening condition
-Tube thoracostomy with a size 28 to 32 french chest tube.
-Immediate drainage of ≥20 ml/kg ( approximately 1500ml ) is an indication for surgical thoracotomy. Other indications for thoracotomy;
- Shock
- Persistent, substantial bleeding, >3ml/kg/hr
-IV fluid resuscitation
-Closely monitor vital signs
-Confirm or rule out other life-threatening conditions. These are considered when determining the need for thoracotomy.
-Pneumohemothorax- drain with a tube thoracostomy.
-Small collections (<300ml) can be treated with expectant management or needle aspiration and drainage.
-Identify and treat the underlying cause for nontraumatic causes
Complications
- Trapped lung
- Pleural empyema
- Fibrothorax